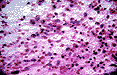
INTRAOPERATIVE MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION:
The stereotatic biopsy was subjected to intraoperative consultation. Touch preparations stained with hematoxylin and eosin revealed the presence of a hypercellular lesion composed of large highly atypical cells lacking nucleoli. Also present were numerous small cells with dense small nuclei and scant cytoplasm (IMAGE 5).
INTRAOPERATIVE DIAGNOSIS:
Microscopic examination of material subjected to formalin fixation, paraffin embedding and hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed the presence of clusters of highly atypical cells, some large with pleomorphic large hyperchromatic nuclei, moderate amounts of eosinophilic cytoplasm and inconspicuous nucleoli. Scattered small cells with dense small nuclei and little cytoplasm were also seen. The cells were found in a fibrillary, neuropil-like background (IMAGE 6 AND IMAGE 7). Foci of mucinous material were also seen. Numerous atypical mitoses (IMAGE 8), karyorrhexis and abundant necrosis were evident (IMAGE 6).
Immunostaining for CD45 (common leukocyte antigen), placental alkaline phosphatase (PLAP), alpha fetoprotein (AFP), beta human chorionic gonadatrophin (bHCG), neurofilament (IMAGE 9) and thyroglobulin was negative. Immunostaining for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) (IMAGE 10) and synaptophysin (IMAGE 11) showed numerous positive large cells. Immunostaining for Ki-67 proliferation protein using the MIB-1 antibody showed a very high proliferation rate. Labelling index was approximately 30% (IMAGE 12).
ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC EXAMINATION:
Ultrathin section preparations showed the presence of abundant filopodia and rare intercellular junctions but no definitive synapses. No intermediate filaments were observed. (IMAGE 13, IMAGE 14 and IMAGE15)
INTRAOPERATIVE CEREBROSPINAL FLUID CYTOLOGY FINAL DIAGNOSIS: