GENETIC TESTING
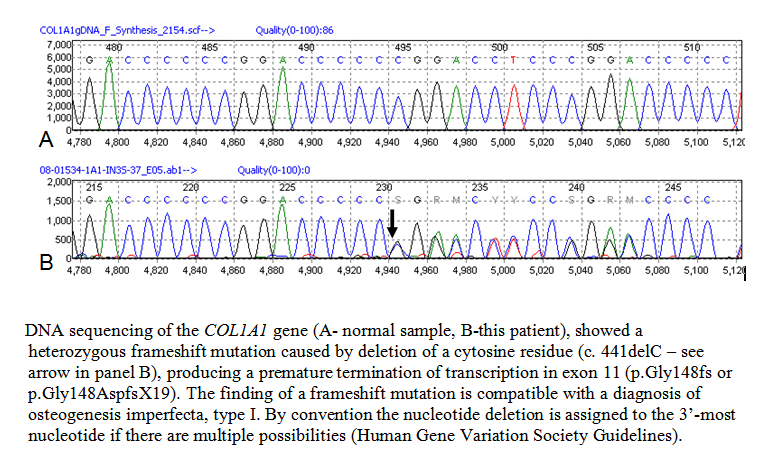
DNA SEQUENCING OF COL1A1 AND COL1A2 GENES

ASSAY PRINCIPLE AND INTERPRETATION
DNA was extracted from skin fibroblasts using standard procedures. COL1A1 and COL1A2 genes were then amplified by PCR, followed by mutation identification by DNA sequencing. DNA sequencing methods were first developed more than 20 years ago with the publication of chemical cleavage (Maxam-Gilbert) and dideoxynucleotide termination (Sanger) approaches. The Sanger method became the standard because of simplicity, speed and ability to sequence all 4 nucleotides in a single high resolution gel or capillary 'pass.' Using a suitable primer, DNA polymerase copies a single stranded product from either the sense or antisense strand in the presence of a mix of dNTPs and ddNTPs. Elongation stops when a ddNTP base is encorporated (ddNTPs lack an hydroxyl group at the 3-carbon so elongation of the sugar phosphate backbone does not occur). ddNTPs are labeled with distinct fluors, thus the presence of a given fluor at a particular fragment length identifies the nucleotide(s) at that position in the template.