![]() Contributed by Jansen N Seheult, MB, BCh and Octavia M Peck Palmer, PhD
Contributed by Jansen N Seheult, MB, BCh and Octavia M Peck Palmer, PhD
CLINICAL HISTORY
A 76 year-old lady presented to the emergency department with a one-week history of progressively worsening generalized edema, fatigue, intermittent chest tightness, mild nausea and decreased exercise tolerance along with 22-lbs unintentional weight gain over the prior four weeks. Significant background history included hypertension, gastro-esophageal reflux disease, hypothyroidism, Crohn's disease and bilateral lumpectomies and radiotherapy for ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). Relevant medications included levothyroxine, losartan, adalimumab, omeprazole, ergocalciferol, calcium carbonate, folic acid and cyanocobalamin.
On admission, the patient was hypertensive (BP 190/92 mmHg) with a pulse rate of 88 beats per minute, respiratory rate of 18 breaths per minute and oxygen saturation of 92% on room air. Cardiac examination revealed a regular rate and rhythm, grade 2 systolic murmur in the mitral area and right upper sternal border, prominent second heart sound, S4 gallop and elevated jugular venous pressure (11cm). Targeted physical examination also revealed bibasilar pulmonary crepitations, moderately distended abdomen, no suprapubic or costovertebral angle tenderness, 3+ pitting edema to the knees bilaterally and 2+ pitting edema in hands bilaterally.
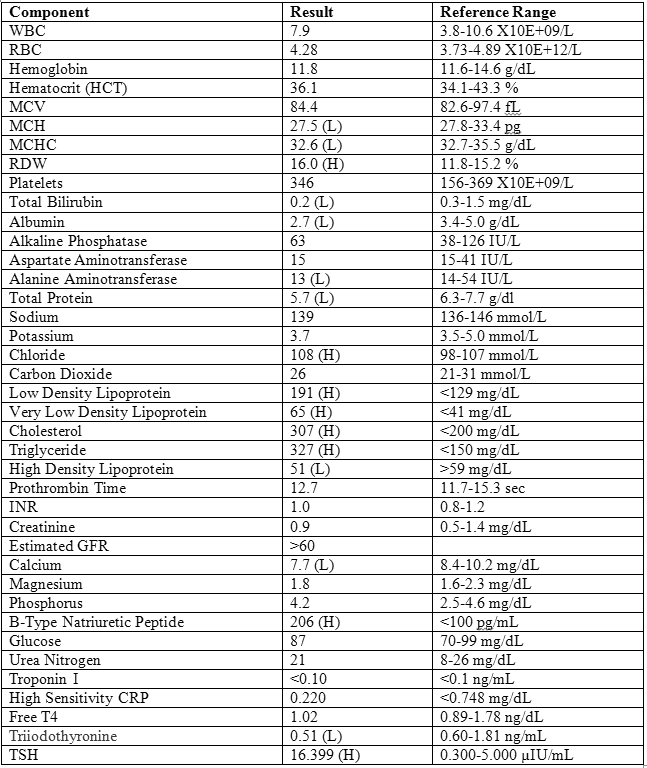
Urinalysis demonstrated proteinuria (greater than 1000 mg/dL), 2+ hematuria and rare bacteria. Spot urinalysis performed on the AU5800 analyzer (Beckman Coulter, CA) on admission produced the following results: urine protein 2200 mg/dl, creatinine 215.6 mg/dl, albumin 17.6 mg/dl (<1.9 mg/dL) and albumin/creatinine ratio 81.6 mg/g (15-37 mg/g creatinine). Other admission laboratory investigations are shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Admission laboratory results
Urine protein electrophoresis (UPEP) did not identify a monoclonal band, as shown in Figure 1.
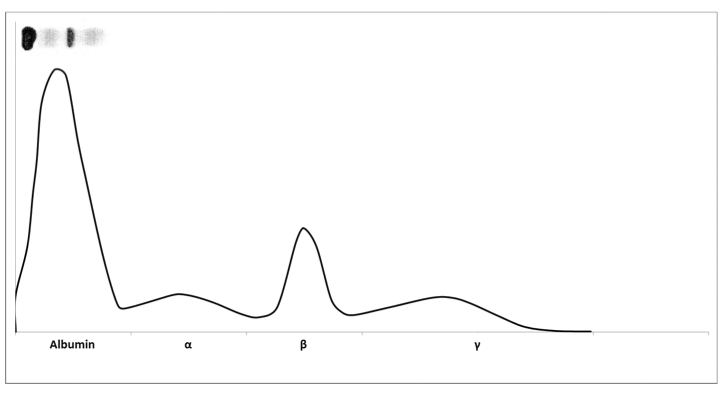
Figure 1: Urine protein electrophoresis.
The Clinical Chemistry department was contacted to investigate the discrepancy between the spot urine total protein and albumin results on the AU5800 analyzer (Beckman Coulter, CA) and the UPEP findings due to the clinical suspicion of nephrotic syndrome.
Repeat analysis of the spot urine sample with serial dilutions (x10, x20) was performed on the AU680 analyzer (Beckman Coulter, CA) with the following results:
Straight Urine Albumin = >30.0 mg/dL
Straight Urine Total Protein = >150 mg/dL
Urine Albumin x10 = >300 mg/dL (autodilution x5 by the instrument = >1500)
Urine Albumin x20 = >600 mg/dL (autodilution x5 by the instrument = 1572)
Urine Total Protein x10 = >2000 mg/dL
Urine Total Protein x20 = 2340 mg/dL
A fresh spot urine sample was also analyzed on the AU680 analyzer with the following results:
Straight Urine ALB = >30.0 mg/dL
Urine Albumin x10 = >300 mg/dL (autodilution x5 by the instrument = 1448)
Urine Albumin x20 = >600 mg/dL (autodilution x5 by the instrument = 1526)
Urine TP x10 = >2000 mg/dL (autodilution x5 by the instrument = 2220)
Urine TP x20 = 2200 mg/dL
When the fresh sample was analysed on the AU5800 analyzer, the albumin results were again below the upper limit of detection:
Straight Urine Albumin = 26.0 mg/dL
Straight Urine Total Protein = >150 mg/dL
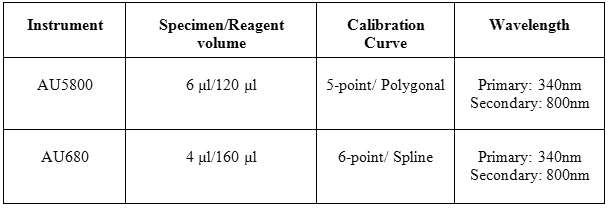
The test parameters for the Urine Microalbumin assay performed on both the AU5800 and AU680 are compared in Table 2.